The Cloud has revolutionized computing, offering flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency. But with these benefits comes an inherent complexity when it comes to security. Two terms frequently thrown around in this context are "cloud security" and "shared responsibility." They are intertwined, yet distinct, and understanding their differences is crucial for anyone venturing into the Cloud.
We've built a platform for Cloud Detection & Response in AWS, Azure, and GCP you can grab a demo here. You can also download free playbooks we've written on how to respond to security incidents in AWS, Azure, and GCP.
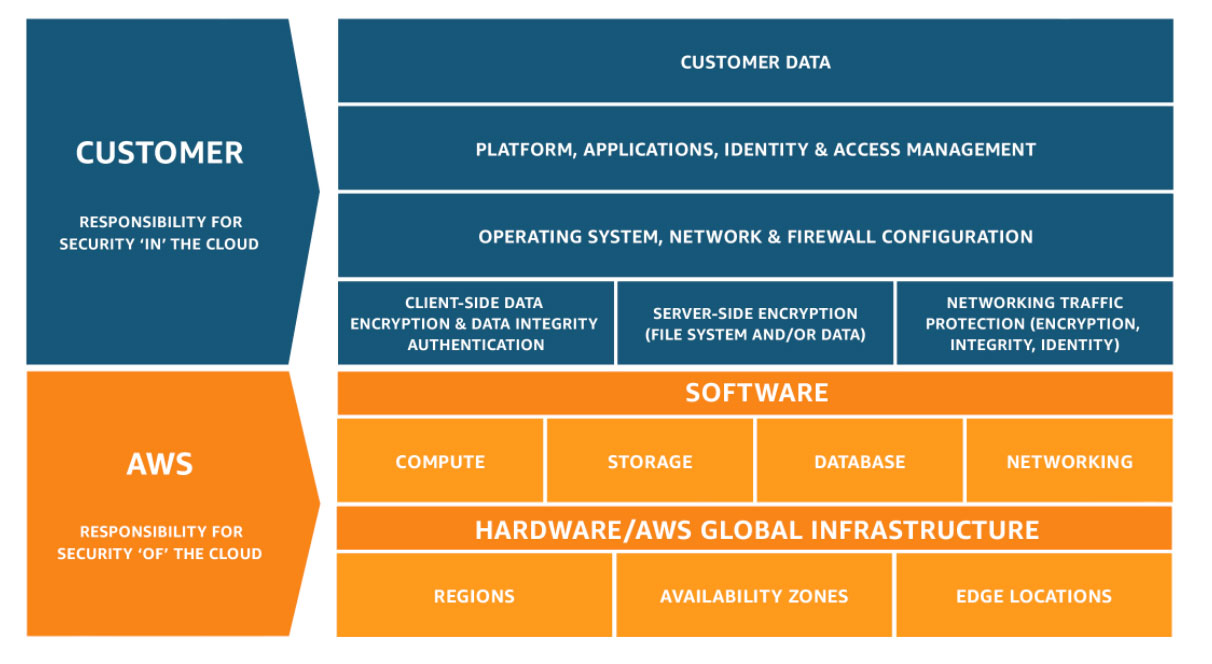
Source: AWS
Cloud Security: The Big Picture
Cloud security encompasses the broad spectrum of practices and technologies employed to protect data, applications, and infrastructure hosted in the Cloud. It's the overarching umbrella that covers various aspects like:
Data security: Encryption, access controls, and data loss prevention strategies to safeguard sensitive information.
Infrastructure security: Securing the underlying physical and virtual infrastructure, including servers, networks, and storage systems.
Application security: Protecting applications deployed in the Cloud from vulnerabilities and cyberattacks.
Identity and access management (IAM): Controlling who can access Cloud resources and what they can do with them.
Incident response: Having a plan for detecting, mitigating, and recovering from security breaches.
Shared Responsibility: Dividing the Cybersecurity Pie
While cloud providers implement robust security measures for their infrastructure, the "shared responsibility model" dictates that the security burden is split between them and the customer. It's like a shared apartment; the building owner maintains the plumbing and wiring, but tenants are responsible for keeping their own space clean and secure.
The specific division of responsibility varies depending on the Cloud service model (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) chosen. Generally, the provider takes care of:
Physical infrastructure security: Securing the data centers and hardware that host the Cloud services.
Platform security: Patching vulnerabilities and protecting the underlying platform for PaaS and SaaS offerings.
Operational security: Implementing best practices for system administration and access control.
Customer responsibilities, meanwhile, typically include:
Data protection: Encrypting sensitive data, managing access controls, and implementing data loss prevention measures.
Application security: Securing their own applications deployed in the Cloud, including patching vulnerabilities and using secure coding practices.
Identity and access management: Configuring who has access to their Cloud resources and what they can do.
Incident response: Having a plan for responding to security incidents that affect their data or applications.
So, the key difference lies in scope:
Cloud security defines the entire domain of securing the Cloud environment, encompassing both provider and customer responsibilities.
Shared responsibility specifies the division of security tasks between the cloud provider and the customer, outlining who's accountable for what.
Understanding this distinction is crucial for:
Choosing the right Cloud service model: Different models allocate security responsibilities differently, so aligning your needs with the model's security commitments is essential.
Implementing effective Cloud security practices: Knowing what you're responsible for allows you to focus your resources on securing your own data and applications.
Building a strong security posture: A collaborative approach to security with your cloud provider is key to maximizing your defenses.
By demystifying these concepts, you can navigate the Cloud with confidence, ensuring your data and applications remain secure while reaping the numerous benefits this transformative technology offers.
Remember, cloud security is not a spectator sport. Both providers and customers have roles to play, and understanding the shared responsibility model is the first step towards building a robust and resilient Cloud environment.
I hope this blog post clarifies the difference between cloud security and shared responsibility. Feel free to ask any further questions you might have!
